Air and street pollution by plastics is a global threat to our planet and affects enormously the environment. This is even more so the case when it concerns the ocean where plastic garbage is dangerous to marine life and interrupts people’s activity. When the wastes have degraded, toxic compounds leach into the environment much into the dumps. Recycling however has a crucial role to play in mitigating this since it avoids the amount of waste that ends up in the seas and dumpsites retained, saves on resources and the degree to which new plastic is called for. This is where General rubbish disposal companies such as Skip Hire Cheshire, recycling firms, and competent elimination of substandard plastic waste disposal bodies are useful.
The Pollution Scale for Plastic
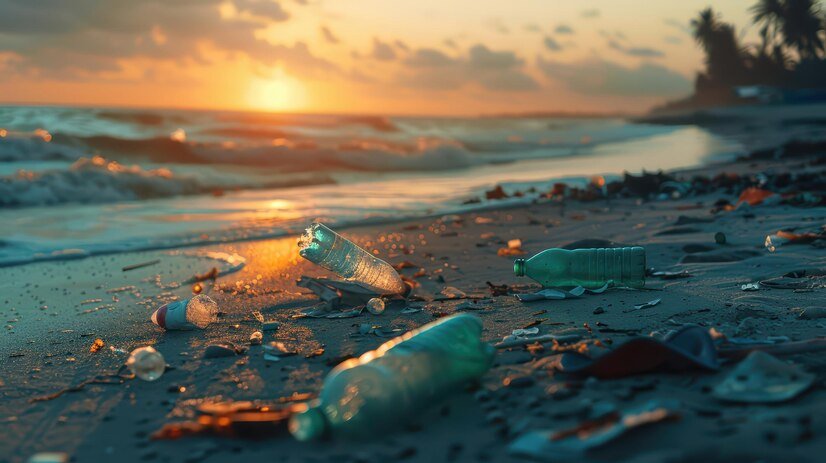
Without a doubt, pollution by plastics is among the most significant problems in the sphere of environmental protection on the global level. At present, approximately millions of tons are produced with the major part of it being dumped. This study stated that the UN points out that 8 million tons of plastic waste find their way into the seas annually to create great whirlwinds of debris. These plastics take roughly 300 years to decompose and when they do so, they are in the form of microplastics which find their way into societies’ food chains.
Environmental Effects
The effects or results of pollution by plastics on the environment are as follows; in aquatic ecosystems, it is rather hazardous because it stuns animals into eating the plastics thinking that they are food and therefore die of hunger, and suffocation. Sea turtles, seabirds and fish are some of the species that are most affected by this type of pollution. Plastic garbage also poses a threat in that it is likely to trap animals, which are immobile and are likely to be harmed or killed. On land, the impacts of plastic pollution are; deforestation, polluted soil and water. When plastics decompose, they emit toxic gases which seep into the ground and water outlets to affect wild life and any other vegetation.
The Disturbance of Ecosystems
Because plastic pollution modifies habitats and food chains, it disturbs organisms. Plastic waste builds up on the seafloor and in coral reefs in aquatic habitats, suffocating marine life. Plastic garbage on land can alter ecosystem diversity by obstructing sunshine and stunting plant growth. As plastic degrades into microplastics, a variety of creatures can consume these tiny bits, exacerbating the problem along with the food chain.
Risks to Human Health
From the pollution of plastics, the welfare of humans is greatly endangered. Some of the groups of products that have been found to contain microplastics include food, drink water, and even the air that we breathe. It presumably has toxic chemicals such as phthalates and biphenyl A (BPA) associated with cancer, endocrine disorders and hormonal imbalances. While the comprehensive effects of Microplastic toxicity are still the subject of the research the dangers are rather concerning.
An Indirect Effect on Global Warming
The manufacturing and disposal of plastics emit pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, into the environment and exacerbate climate change. Plastic is mostly made from petroleum, whose extraction uses a lot of energy and produces a lot of carbon dioxide. Furthermore, burning or being outdoors releases carbon dioxide and methane from plastic garbage, exacerbating climate change.
How Can Plastic Recycling Benefit the Environment?
There are multiple ways in which plastic recycling benefits the natural world. We have identified six of them. Have a read:
Energy Conservation
Recycling requires less energy than manufacturing new, virgin polymers.
Decreased Demand for Raw Materials
Plastic recycling decreases the demand for fresh raw materials from the earth by reusing previously processed products and protecting the planet’s resources. This may help limit the amount of heat-trapping gases released into the atmosphere. It also keeps more waste from ending up in landfills.
Reduced Usage of Fossil Fuels
Plastic manufacture requires a great deal of oil. Despite recycling utilising fossil fuels, it is substantially less than the quantity used to produce new plastics.
Read more: https://classroom6x.co.uk/how-to-choose-a-good-optician-key-factors-to-consider/
Final Words
The plastic pollution situation is complicated, necessitating a variety of remedies. While minimizing your plastic footprint is a crucial part of the solution, it needs to be accompanied by larger systemic changes such as policy structures, monetary incentives, enhanced infrastructures and new business models.
Read more articles related to health at Classroom 6x.